Michiel (Michael) Coxie (1499-1592) was a prolific and successful artist named ‘the Flemish Raphael’ by his contemporaries. Living under the protection of noble people, he worked on paintings, tapestry designs, and engravings. His extraordinary talent allowed him to become a wealthy man who kept things on an even keel during the Eighty Years’ war. He remained a sought-after artist even in his nineties. The artist died after falling off a scaffold while working on the restoration of ‘the Judgment of Solomon‘ in the Antwerp City Hall.

Fig. 1. Portrait of Coxie by Simon Frisius (Wikipedia.org)
Obscured But Outstanding
The early years of Coxie remain obscured. The year of his birth can be defined only indirectly, as well as the place where he was born. The masters from whom he received his training are also unknown. Some biographers point at the Brussels master Bernard van Orley, as Coxie shared with him the favor of Flemish cardinal Willem van Enckevoirt. The argument is that van Orley could introduce his pupil to the patron. After van Orley died in 1541, Coxie was commissioned to complete his work on stained glass windows of the Brussels cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula.
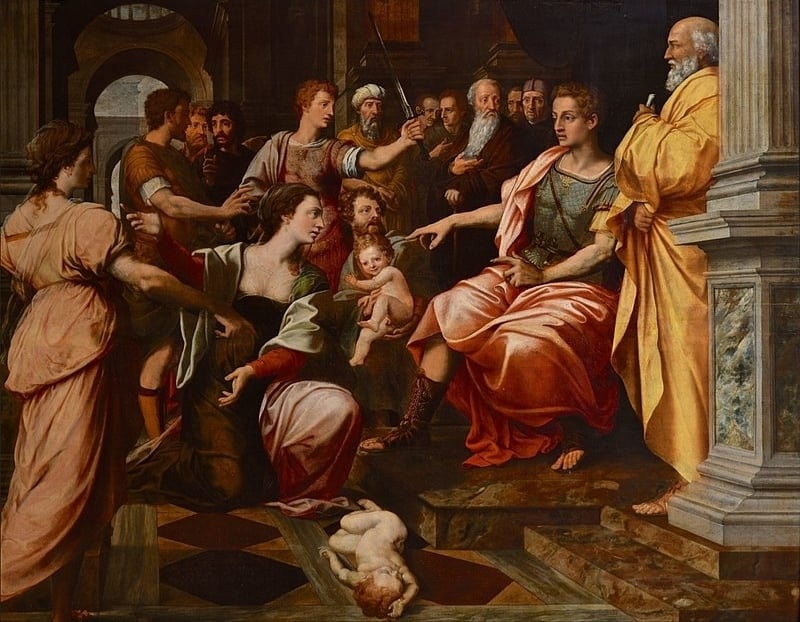

Fig. 2. The Judgment of Solomon (Wikipedia.org)
Travel to Italy
Coxie achieved his notoriety as Flemish Raphael after his residence in Italy. Being ordered by Willem van Eckevoirt to paint frescos in the Santa Maria dell’Anima, the artist had to study fresco technique. Had accomplished the order, Coxie became the first painter to be included in the Compagnia di San Luca, the guild of painters and miniaturists in Rome. He stayed in Italy approximately from 1527 to the 1540s. In 1539, he traveled back to the fatherland. While being abroad, Coxie also produced designs for Italian engravings, including the series ‘The Loves of Jupiter‘ and 32 plates on the story of Amor and Psyche. These designs were used by many engravers such as Agostino Veneziano, Master of the Die, Marcantonio Raimondi, Virgil Solis.
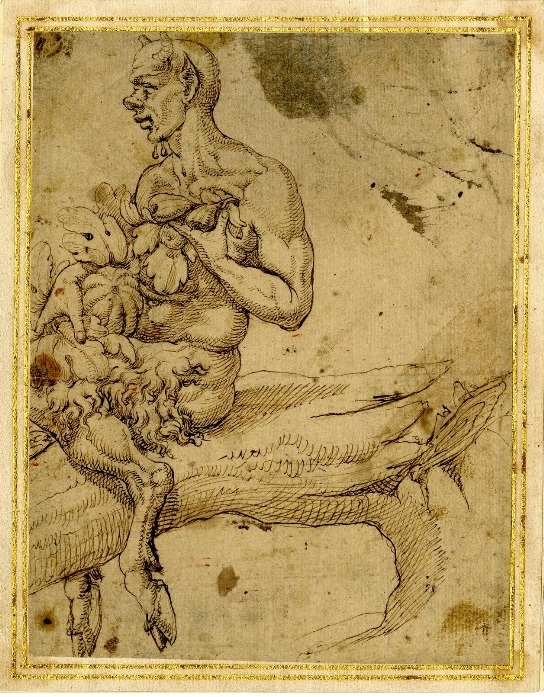
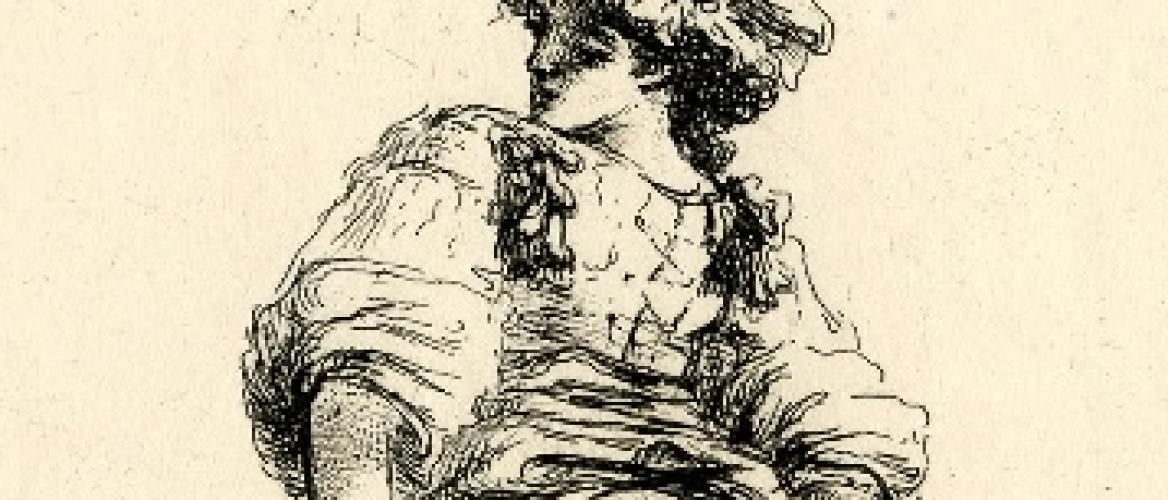
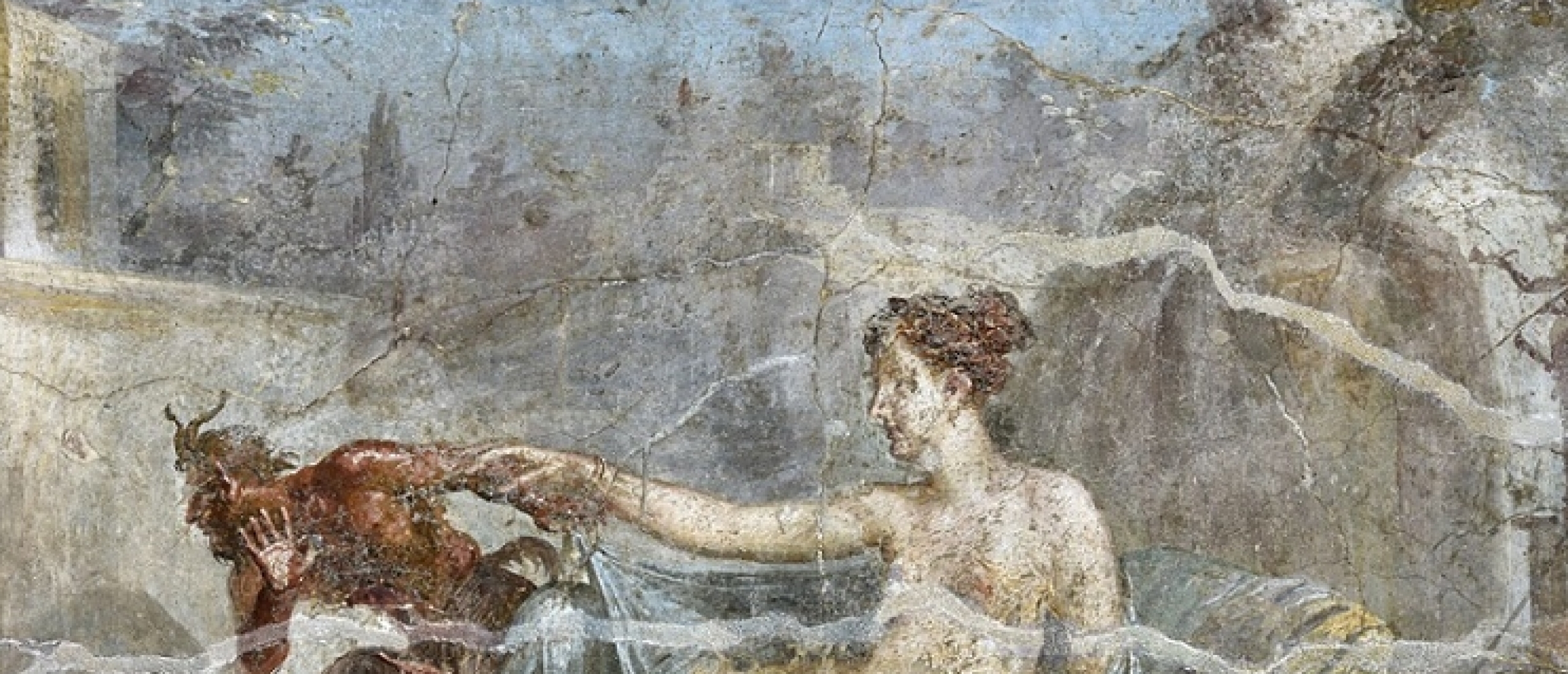
Fig. 3. Satyr straddling a tree branch, attrib. to Coxie (britishmuseum.org)
The Loves of Jupiter
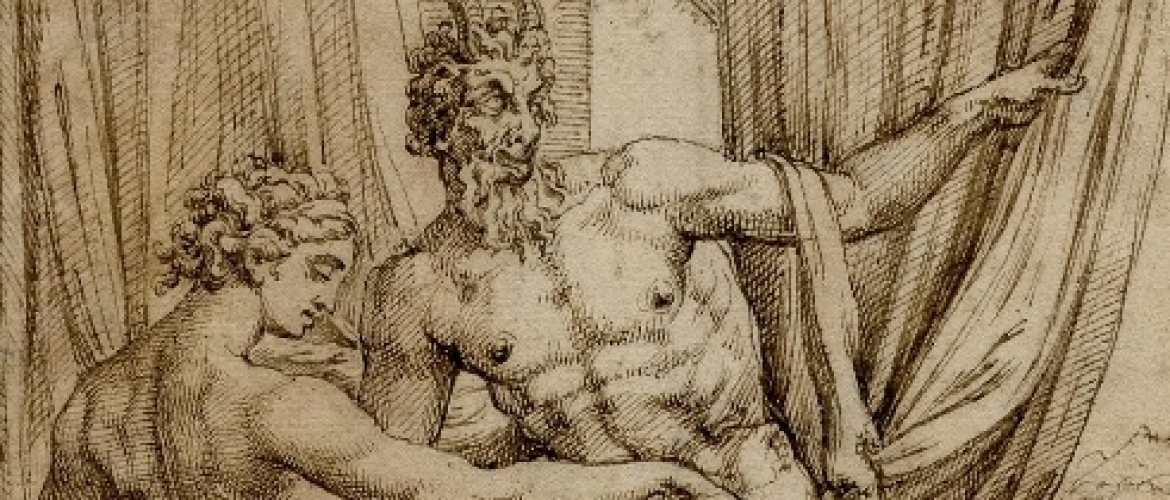
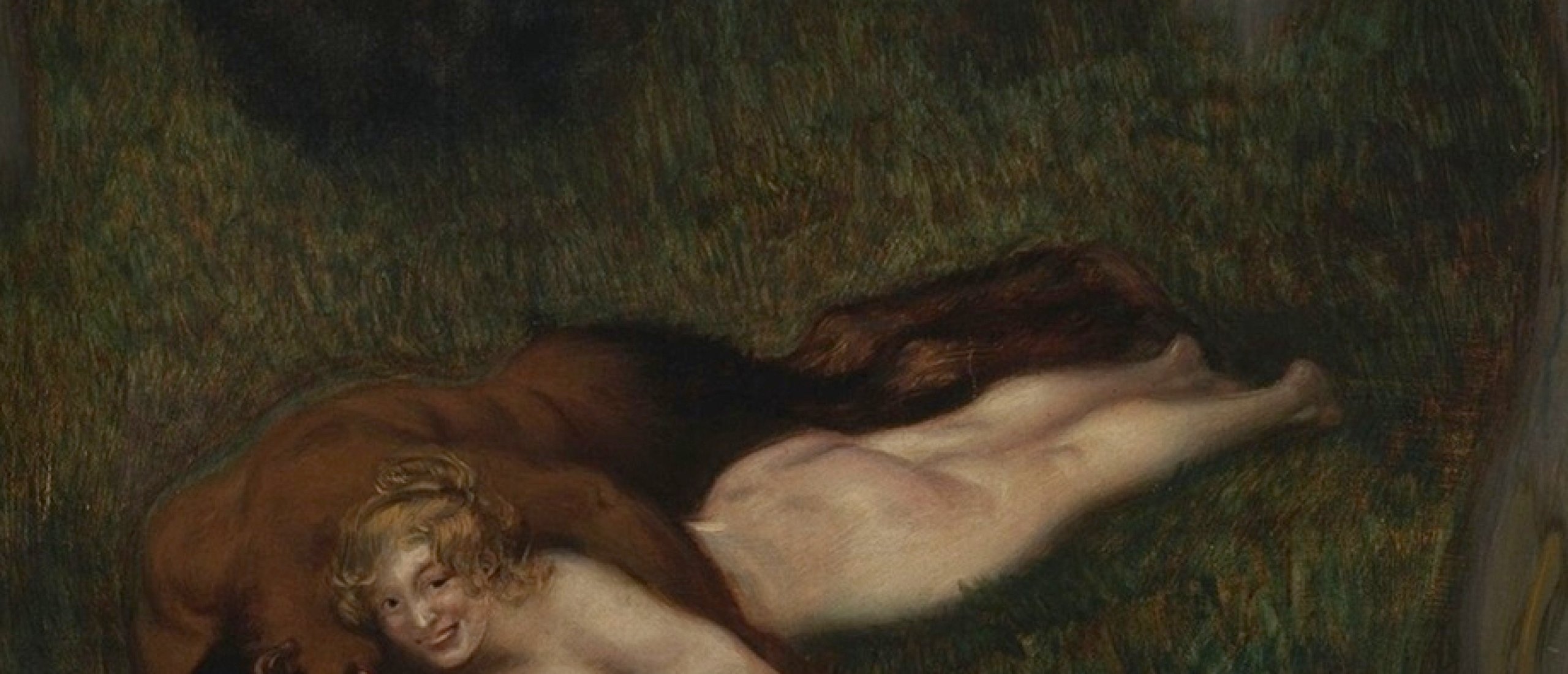
The set of designs depicting Jupiter’s love affairs consists of depictions of well-known Greek myths. Among them are the story of Leda and the swan, Ganymede’s and Europe’s abduction, misfortunes of Io, whom Jupiter had to transform into a heifer to hide her from Juno, the temptation of chaste Diana’s companion Callisto when Jupiter disguised himself as a goddess of the hunt to approach the nymph, and so on. The less-known plot is Jupiter’s affair with Antiope, the daughter of the river god Asopus. Jupiter copulated with her in the form of a satyr. Original Coxie’s design weirdly lacks the eagle that was a constant attribute of the god. It can be seen in an engraving by Virgil Solis. The most spectacular scene is the copulation of Jupiter and Phoenician princess Semele in flames. Willing to perish a mortal woman, Juno persuaded her to ask Jupiter to appear in his real shape. Curious Semele did this and died in fires and flashes, giving birth to Dionysus.

Fig. 4. Leda and the swan (thebritishmuseum.org)

Fig. 5. Ganymede’s abduction (thebritishmuseum.org)
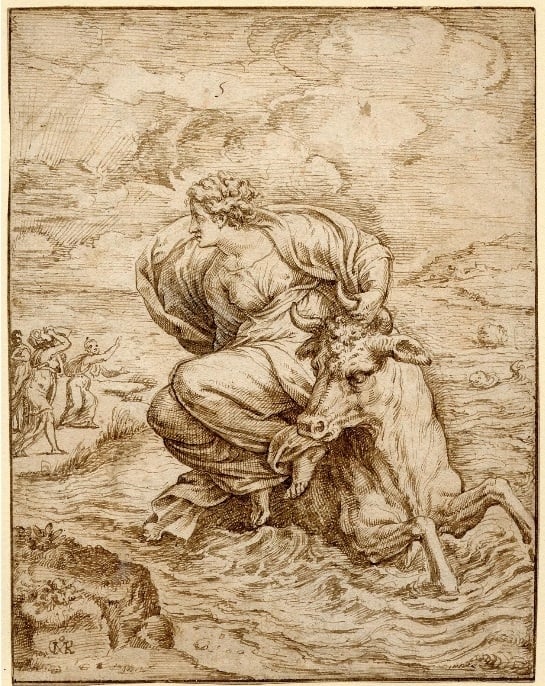

Fig. 6. Europe’s abduction (thebritishmuseum.org)

Fig. 7. Jupiter transforms Io into a heifer while Juno’s watching (thebritishmuseum.org)
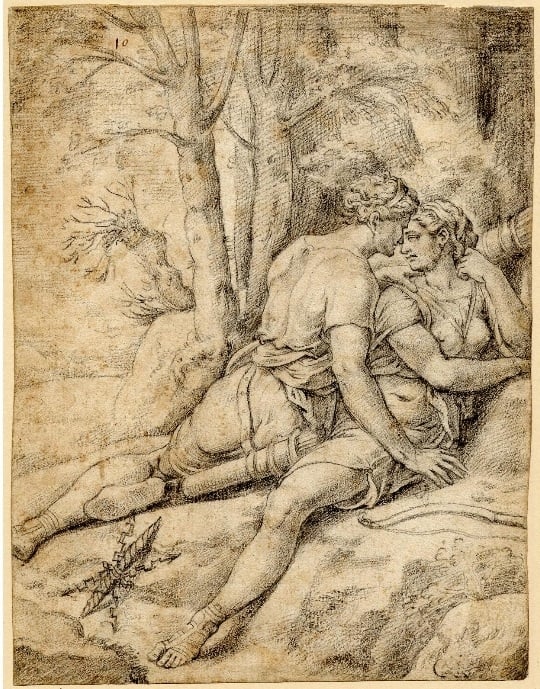

Fig. 8. Jupiter disguised as Diana seduces Callisto (thebritishmuseum.org)
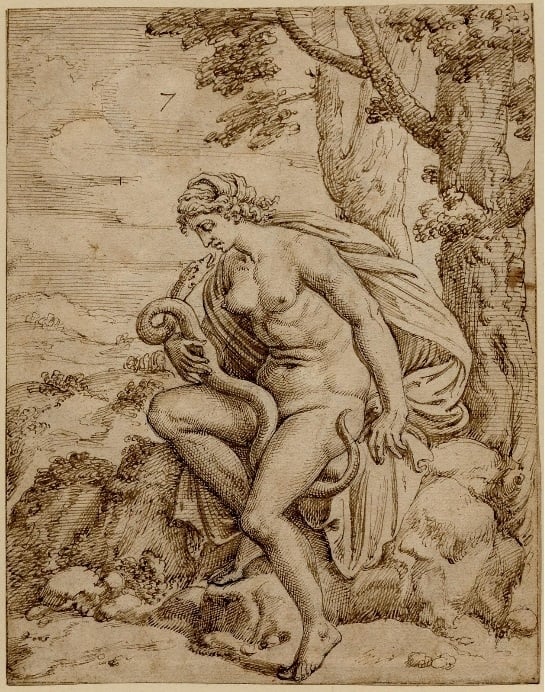

Fig. 9. Jupiter seduces Proserpine, the spouse of Hades, in a shape of a serpent (thebritishmuseum.org)
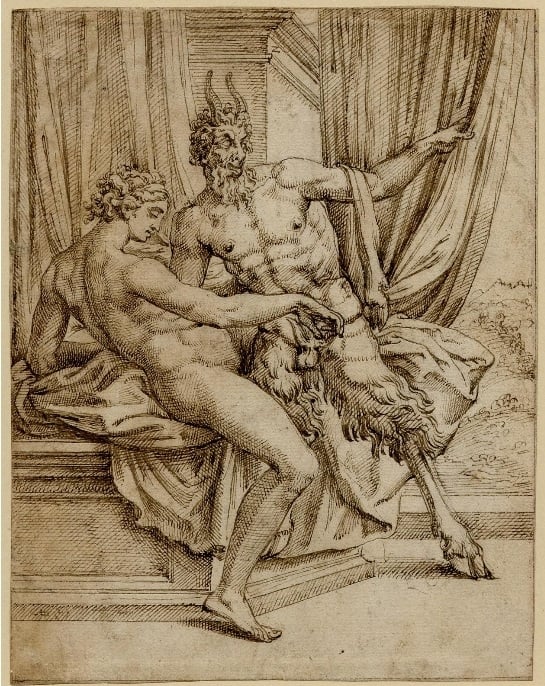

Fig. 10. Jupiter as a satyr and Antiope (thebritishmuseum.org)
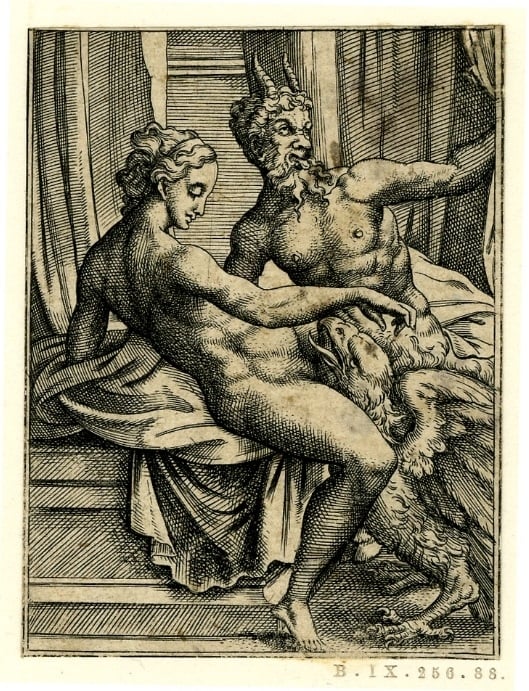

Fig. 11. Jupiter with the eagle covering his genitalia (engraving by Virgil Solis based on Coxie’s design), britishmuseum.org
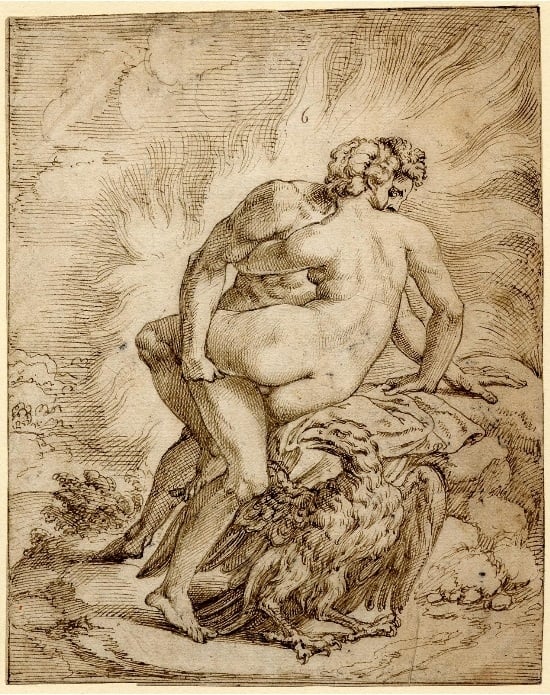

Fig. 12. Jupiter and Semele in flames (thebritishmuseum.org)
Cupid and Psyche
The story of Cupid and Psyche was a novel included in 'The Golden Ass' by Apuleius. Psyche was a princess whose beauty caused the anger of Venus as folks considered Psyche an earthly incarnation of the goddess. Venus ordered her son to make Psyche fall in love with a disgusting monster. Apparently, Cupid took this literally as he had a reputation of an unbearable infant terriblé whose arrows often made gods feel uneasy. Thus, the son of Venus wounded himself with his dart. The tale full of trials for Psyche, who receives immortality in the end, has many meanings. It can be treated as an allegory of the human soul searching for the god and as the story of an evil mother-in-law, proving a widespread opinion that men often marry women similar to their mothers.
The Husband as a Kid
The latter statement seems to be strangely supported by Coxie designs as here we see an encounter of adult Psyche with Cupid traditionally depicted as a kid. Lots of artists referring to this theme pictured characters as counterparts, sometimes as two kids. Meanwhile, Eros wasn't just a weaponed irresponsible kid. Some ancient authors regarded him a primary deity. Socrates described Eros as a half-human half-celestial daemon.
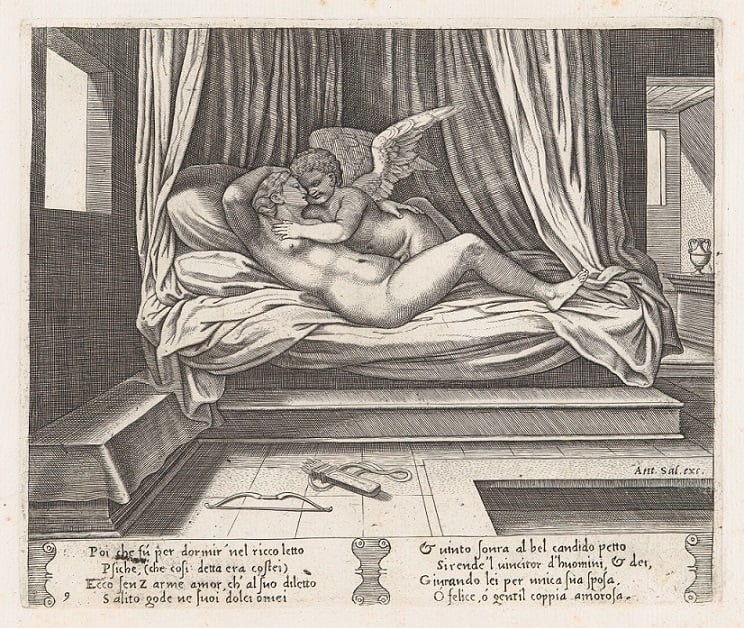
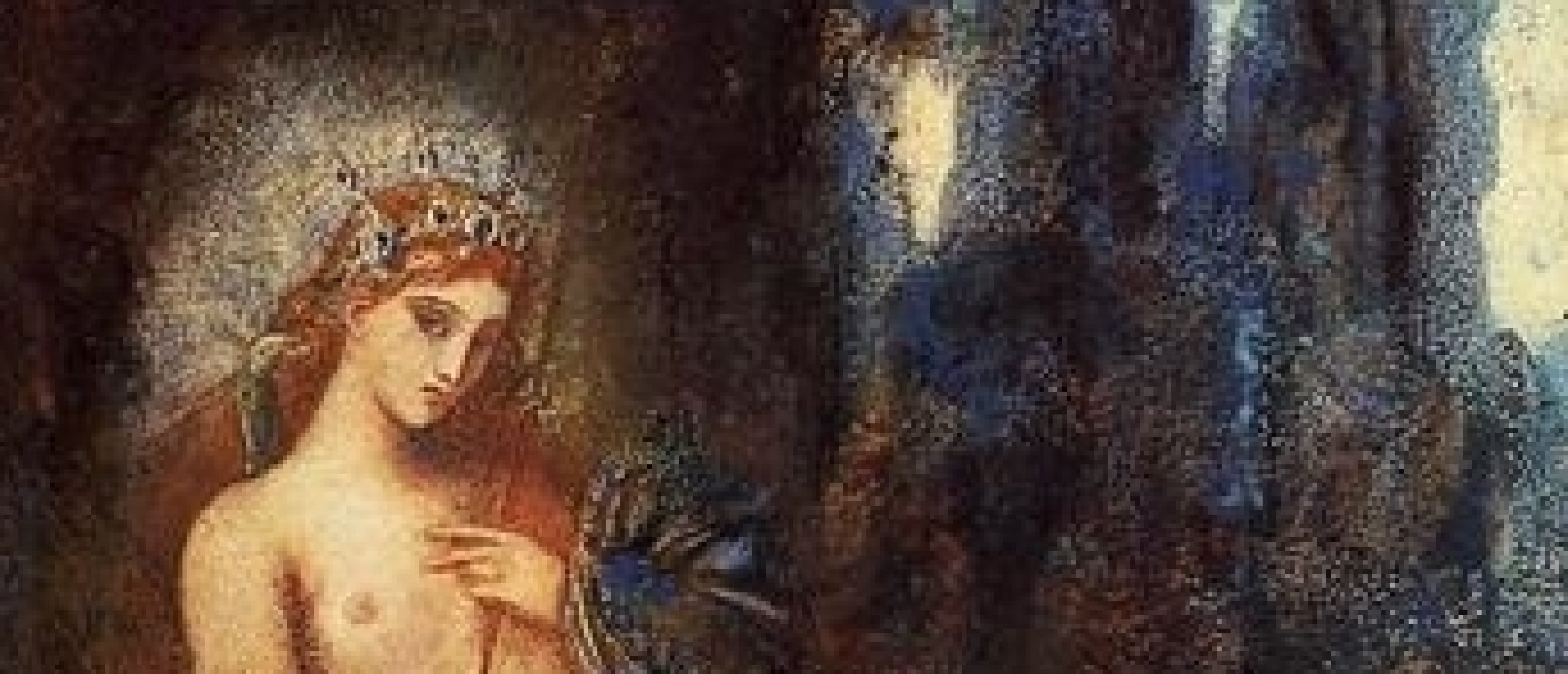
Fig. 13. Psyche and invisible Cupid on a bed (Wikipedia.org)
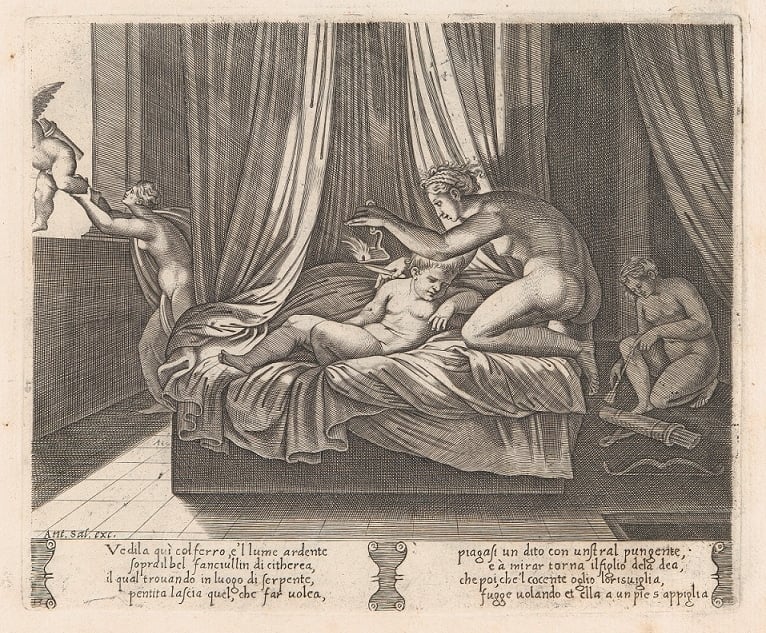
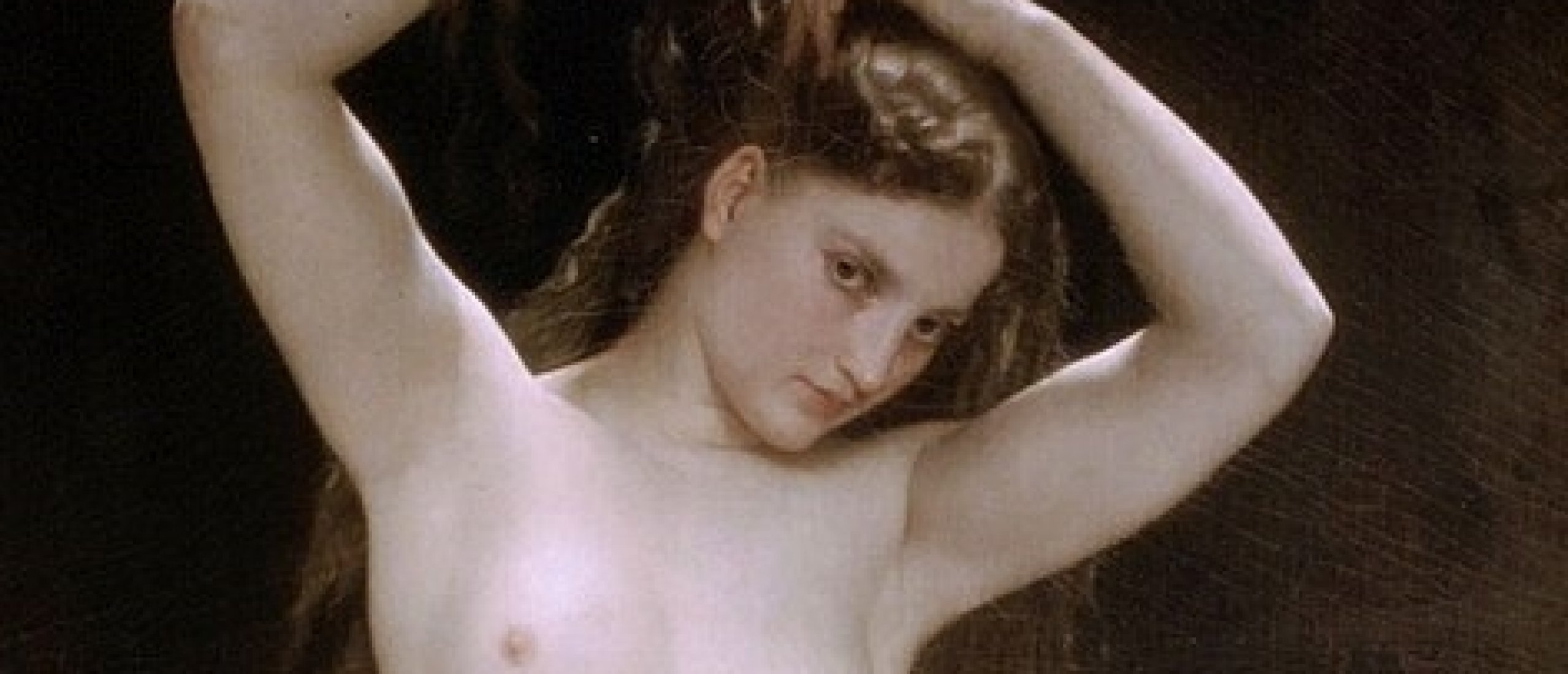
Fig. 14. From right to left: Psyche occasionally wounds herself with an arrow, discovers who her husband is, and tries to hold flying Cupid down (Wikipedia.org)
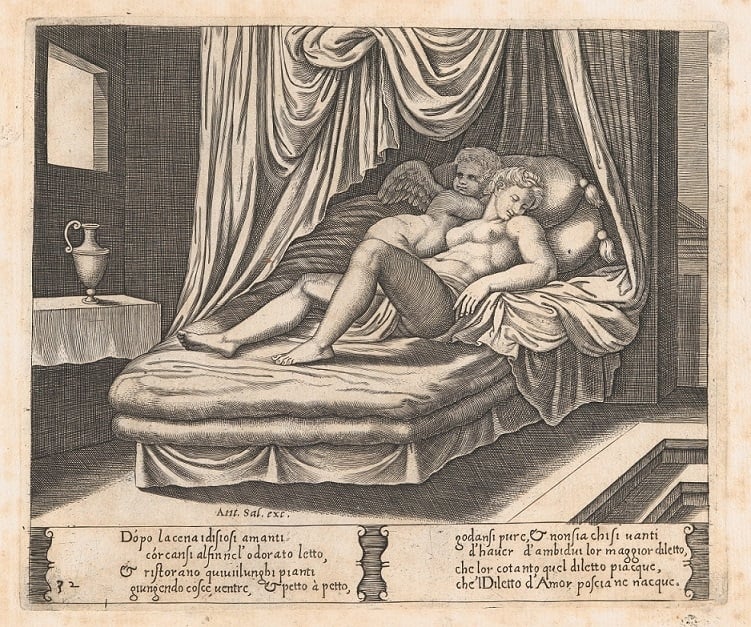
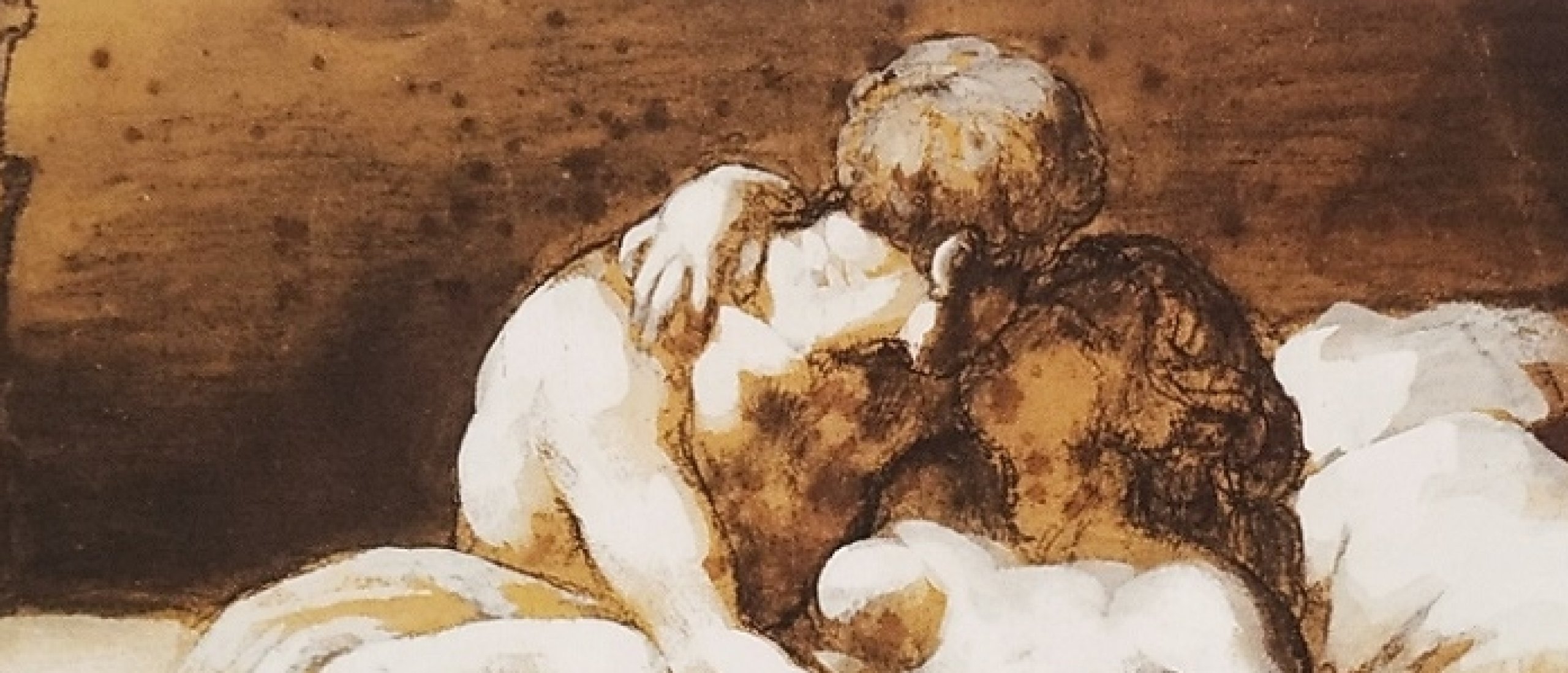
Fig. 15. Cupid and Psyche on a nuptial bed (Wikipedia.org)
Click HERE for the loves of the Gods by Renaissance artist Guilio Bonasone
Sources: Wikipedia.org; britishmuseum.org










